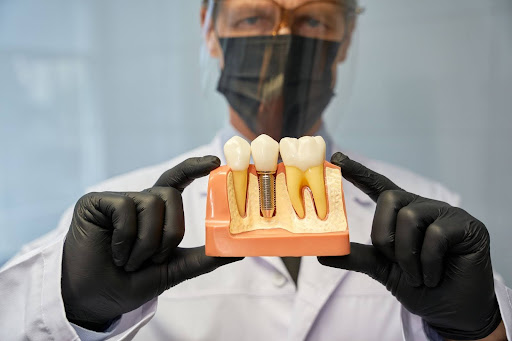
How Long Do Dental Implants Last?
Dental implants are one of the most advanced and reliable solutions in modern dentistry for replacing missing teeth. Patients considering this procedure often ask a critical question: How long do dental implants last? The answer is not straightforward, as the lifespan of a dental implant depends on several factors, including the quality of the implant, the patient's oral hygiene, overall health, and the level of care the implant receives over time. This blog explores the components, expected longevity, and variables that impact the lifespan of dental implants, along with expert insights to help you make informed decisions about your dental health.
Why Dental Implants Are a Long-Lasting Tooth Replacement Solution
Dental implants are widely regarded as a long-term solution for missing teeth. Unlike dentures or bridges that rest on the surface or use adjacent teeth for support, dental implants are anchored into the jawbone through a titanium post. The anchor creates a stable and durable foundation that mimics the function of a natural tooth root. Due to this design, dental implants can last for decades or even a lifetime with proper care. However, their longevity relies on both biological and lifestyle factors that will be examined in more depth throughout this blog.
What Are the Main Components of Dental Implants?
To fully understand how long dental implants last, it's essential to break down the three main components: the implant post, the abutment, and the crown. The implant post, usually made of titanium, is surgically embedded into the jawbone and integrates with the bone over time in a process known as osseointegration. The abutment is a connector that holds the crown in place on the post. Lastly, the dental crown is the visible part of the implant that functions like a natural tooth. While the titanium post can last a lifetime, the crown and abutment may need replacement after ten to 15 years due to wear and tear.
How Long Do Dental Implants Typically Last?
Under ideal conditions, dental implants can last 25 years or more. In many cases, patients enjoy their dental implants for a lifetime without issues. According to studies, the success rate of dental implants after ten years is approximately 90-95%. It’s important to differentiate between the implant itself (the titanium post) and the prosthetic crown. While the post can remain stable indefinitely, the crown may require replacement or adjustment due to regular use, especially if it's subjected to excessive force or improper care. Therefore, while the structure is built to last, longevity also depends on maintenance.
Common Reasons Dental Implants Fail Over Time
Although dental implants have a high success rate, a few issues can contribute to failure if not addressed promptly. Being aware of these risk factors allows patients and providers to take preventive action and protect long-term implant success:
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting daily care can lead to plaque buildup, inflammation, and peri-implantitis, ultimately weakening the implant’s foundation. Over time, this can result in bone loss and eventual implant failure if not treated promptly. Establishing a consistent brushing and flossing routine is crucial for maintaining the health of the surrounding tissues.
Smoking or Tobacco Use
Smoking reduces blood flow and delays healing, increasing the risk of implant failure during and after osseointegration. It also weakens the immune response, making the gums more vulnerable to infection. Even occasional tobacco use can significantly reduce the success rate of dental implants.
Inadequate Bone Support
Insufficient bone volume or density can prevent proper integration, primarily if bone grafting isn’t performed when needed. Without a stable foundation, the implant cannot anchor securely, leading to instability over time. Routine imaging and evaluations can help determine if additional bone support is required before placement.
Excessive Bite Force
Clenching, grinding, or chewing on complex objects can place excessive stress on the implant, leading to loosening or fracture. These forces can also damage the surrounding bone or the implant crown itself. Custom night guards or bite adjustments can help minimize the risk in patients with bruxism or TMJ disorders.
Systemic Health Conditions
Conditions like diabetes, osteoporosis, or autoimmune disorders can interfere with healing and compromise implant stability. These health issues may also affect bone density and tissue regeneration, both of which are vital for long-term implant success. Coordinated care with a healthcare provider can improve outcomes for patients with chronic conditions.
Dental Implants and the Role of Oral Hygiene
One of the most significant factors in determining the longevity of dental implants is oral hygiene. Just like natural teeth, implants require daily brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups to maintain their health. Poor oral hygiene can lead to peri-implantitis, a condition similar to gum disease that affects the soft and hard tissues around the implant. If left untreated, this can lead to bone loss and eventual implant failure. Patients who commit to excellent oral hygiene routines can significantly extend the lifespan of their dental implants and avoid complications that shorten their usability.
How Lifestyle Choices Impact the Lifespan of Dental Implants
Lifestyle plays a crucial role in determining the longevity of dental implants. Habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption can impair healing after implant surgery and increase the risk of implant failure. Smoking, in particular, restricts blood flow to the gums and interferes with osseointegration, reducing the implant’s ability to fuse with the jawbone. Similarly, individuals who frequently consume sugary or acidic foods without proper oral care may experience a higher risk of infection or decay in adjacent teeth, which could compromise implant success. Choosing a healthy lifestyle can dramatically influence implant longevity.
Dental Implants and the Importance of Regular Dental Visits
Routine dental check-ups are vital for maintaining the health of your dental implants. During these visits, a dentist will assess the stability of the implant, the condition of the surrounding gum tissue, and the wear on the crown. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that could compromise implant health. Additionally, dental professionals can detect early signs of peri-implantitis or bite misalignment before they develop into significant problems. Biannual visits are typically recommended; however, some patients may require more frequent monitoring, depending on their individual needs and circumstances.
How Dental Implants Compare to Other Tooth Replacement Options
Compared to dentures and bridges, dental implants offer superior longevity, comfort, and function. Dentures often need replacement or adjustment every five to ten years, and they can become uncomfortable over time due to bone resorption. Bridges typically last ten to 15 years and may put stress on adjacent teeth. Dental implants, however, preserve jawbone integrity and function like natural teeth without affecting neighboring structures. This preservation makes them the most sustainable long-term option, especially for individuals seeking permanence and reliability.
Can Dental Implants Last a Lifetime?
Yes, dental implants can last a lifetime—but only with the proper care and conditions. Clinical data suggests that the titanium post has the potential to last indefinitely when properly integrated and maintained. However, the prosthetic crown may require replacement after ten to 15 years due to normal wear and tear. Lifespan also depends on individual factors such as genetics, immune response, bite force, and maintenance habits. While nothing in dentistry is true "forever," implants come as close as possible with excellent outcomes and reliability over the long term.
Signs Your Dental Implants May Need Attention
Being proactive about potential problems can save your implant and preserve surrounding structures. Recognizing warning signs early increases the likelihood of successful treatment and long-term implant health:
Persistent Pain or Discomfort
While mild soreness is normal after placement, persistent pain may indicate an infection or mechanical issues. If the discomfort worsens over time or is accompanied by swelling, it should be evaluated immediately. Ignoring the problem may lead to complications that necessitate surgical intervention.
Gum Inflammation or Bleeding
Redness, swelling, or bleeding around the implant could indicate early signs of peri-implantitis or poor oral hygiene. These symptoms often appear before bone loss occurs and should not be overlooked. Early treatment can prevent more serious damage to the implant and surrounding tissues.
Loosening or Shifting
A secure implant should feel just like a natural tooth—any movement should be assessed by a dentist immediately. Loosening may be due to problems with the abutment, crown, or even the implant's integration with bone. Timely repairs can restore stability and prevent complete implant failure.
Difficulty Chewing
Changes in bite pressure or discomfort when eating may point to an issue with alignment, the crown, or underlying bone. Chewing difficulty can also lead to jaw fatigue or a preference for one side of the mouth. A dentist can assess occlusion and make necessary adjustments to restore balance and alignment.
Visible Bone Loss or Gum Recession
Receding gum lines or visible metal near the gum can suggest deterioration of the tissue supporting your implant. These symptoms may progress gradually and often go unnoticed until serious issues arise. Routine check-ups can detect these changes early and help maintain the implant's integrity.
How Age and Health Conditions Influence Dental Implant Longevity
Contrary to popular belief, age alone is not a barrier to dental implants. Older adults can be excellent candidates as long as they maintain good general and oral health. However, certain medical conditions—such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or cancer treatment—may interfere with healing and bone integration. These factors don’t necessarily rule out implant placement but may require specialized care and more diligent follow-up. A thorough health assessment by your dentist or oral surgeon will determine your suitability for long-lasting implant success.
How Dental Implant Placement Technique Affects Durability
The expertise of the dental professional placing your implant has a direct impact on its longevity. Precise placement is essential for ensuring proper alignment, bite distribution, and osseointegration. Advanced techniques such as 3D imaging and guided implant surgery improve accuracy and reduce complications. Improperly placed implants may lead to uneven stress distribution or nerve damage, increasing the likelihood of failure. Choosing a skilled and experienced implant dentist is one of the most critical factors in ensuring long-term success.
Caring for Dental Implants at Home
Daily care of dental implants is similar to the care of natural teeth. Brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouth rinse help reduce plaque and maintain gum health. Special interdental brushes can help clean around the implant where standard floss might not reach. Avoiding overly abrasive toothpaste and hard foods also protects the crown and abutment. A consistent home care routine can significantly increase the lifespan of your dental implants.
Dental Implants and the Role of Diet in Longevity
Diet plays a significant yet underappreciated role in determining the longevity of dental implants. Nutrient-rich foods that promote bone and gum health—such as leafy greens, dairy, lean proteins, and vitamin-rich fruits—can enhance implant longevity. On the other hand, a diet high in sugar or acidic foods increases the risk of plaque buildup and inflammation around the implant. Hydration is also key, as saliva helps neutralize acids and protect oral tissues. A balanced diet supports not just general health but also the structural integrity of your dental implants.
What to Do If a Dental Implant Fails
Although rare, implant failure can occur and should be addressed promptly. Signs include discomfort, loosening, inflammation, or difficulty chewing. If failure occurs, options may consist of removing the failed implant, performing bone grafting, and reattempting placement after the implant has healed. Success in a second attempt is often higher if the cause of the initial failure is identified and addressed. Early intervention is critical to preserving bone structure and restoring function.
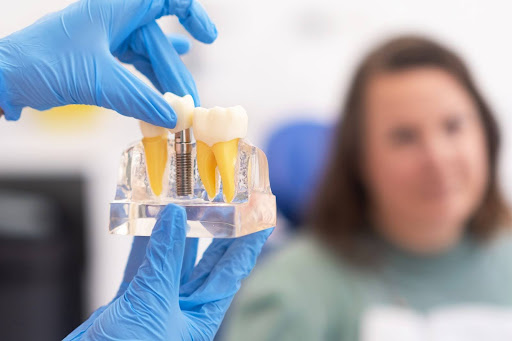
How to Ensure Your Dental Implants Last
Dental implants are one of the most reliable and long-lasting options for tooth replacement available today. Their success is not only rooted in medical technology but also in patient commitment to care. With proper hygiene, routine dental visits, healthy lifestyle choices, and professional oversight, dental implants can last a lifetime. They not only restore function and appearance but also enhance confidence and quality of life. When viewed as an investment in your long-term oral health, dental implants are a decision that continues to pay off year after year.
To learn more about how long dental implants last, visit our Synergy Dental blog.